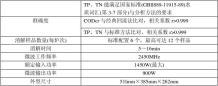
An overview 1. 1 product features a) Closed digestion, overpressure protection, safe and reliable, complete the buzzing prompt after digestion; b) Digestion of various substances: This manual mainly introduces the digestion and testing methods of chemical oxygen demand (CODcr), total phosphorus (TP) and total nitrogen (TN); c) Save time and money, and operate easily and conveniently; d) For digestion of CODcr:  1 It has the ability to resist chloride interference and can measure water samples with CODcr value greater than 50mg/L and chloride ion content up to 10000mg/L;  2 It can measure the low CODcr value below 10mg/L. 1.2 Scope of application and main purposes III (CODCr, TP, TN) microwave digestion device (referred to as the device, the same below). Rapid and efficient digestion and determination of chemical oxygen demand (CODCr), total phosphorus (TP) and total nitrogen (TN) in various surface water, domestic sewage and industrial wastewater. It is widely used in the identification and management of water quality by environmental protection departments, water resources management departments and public health departments at all levels. 1.3 Use of environmental conditions a) Ambient temperature: 5 ~ 40 ° C; b) Ambient humidity: ≤90% RH; c) Atmospheric pressure range: 86kPa ~ 106kPa. 1.4 Working conditions a) The unit shall operate on an AC (220 ± 22) V (50 ± 1) Hz power supply. b) Work system: continuous. Second, the working principle The device adopts the test method and national standard (GBll889-11115-89) water quality vocabulary (Parts 3-7) and analysis method, "Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Method" (third edition) CODcr potassium dichromate method and total phosphorus The potassium persulfate digestion spectrophotometry of total nitrogen is basically the same. The device uses a microwave energy heating method with a frequency of 2450 MHz. Under its action, the dipole molecules in the reaction system will rotate at a high speed, forming intense friction and collision, and the temperature of the reactants will rise rapidly, achieving the ideal effect of high efficiency, fast and low consumption. The device also employs a means of digestion in a closed (sealed) state. One of the advantages is that it can make a certain pressure in the tank to rapidly increase the temperature of the reaction system and shorten the digestion time. Secondly, in the CODcr analysis, it can effectively inhibit the oxidation of chloride ions by potassium dichromate to chlorine, and then add appropriate amount. The mercury sulphate is used as a masking agent to determine the chemical oxygen demand of high-chlorine wastewater. Third, the instrument introduction 3. 1 configuration The device includes one microwave digestion furnace, and six PTFE digestion tanks are randomly arranged (this device can place twelve digestion tanks at a time, and additional PTFE digestion tanks can be added if necessary). 3. 2 specificity The device is designed to digest organic contaminants in water samples and should not be used for other purposes. 3. 3 cooling ventilation Vents are provided at the bottom and top of the unit for heat dissipation and exhaust, and must not be blocked (torn the wrapped furnace film before use). 3. 4 runners, turntables Put the wheel and glass turntable before using the device, and make sure that the turntable is in the center of the wheel and concentric. 3. 5 digestion tank The PTFE digestion tank is designed for this device and cannot be used for other purposes. Only under the reagents and reaction conditions specified in this specification can the pressure protection of the tank be effectively implemented and guaranteed. Fourth, technical characteristics 4.1 Characteristics The device is manufactured for the intended use (1.2) and is used for chemical oxygen demand, total phosphorus, total nitrogen digestion, and testing. 4. 2  Main technical parameters (see Table 1) Table 1 Main technical parameters table 4.3 instructions for use and precautions 4.3 .1 Panel schematic notes: 1 Display shows setting and digestion time 2 “Minute†button to set the digestion time, press “10†and “l†Set "10 minutes" and "1 minute" respectively 3 "seconds" button to set the digestion time, press "10" and "l" Set "10 seconds" and "1 second" respectively 4 Press the button when the “CODcr†button is used for CODcr digestion. 5 "TP/TN" button: press this button (three times) when doing TP and TN digestion. 6 Press the button when the “Start†button activates the microwave circuit 7 “Stop/Cancel†button to stop digestion or Press this button when canceling the set value 4.3 .2 Operation against the panel diagram 4.3 .2.1 Determination of digestion time (see Table 2) 4.3 .2.2 apparatus operating method a) Tighten the digestion tank with the digestion solution, place it evenly on the outer ring of the device turntable, and close the furnace door; b) Press the “Pause/Cancel†button once; c) Press “CODcr†once for CODcr digestion. Press TP/TN three times for TP/TN digestion; d) Press the “minute†button and the “second†button to set the time according to the digestion time specified in “Table 2â€; e) Press the “Start†button once to start the digestion. 4.3 .3 Notes 4.3 .3.1 Do not use the digestion device under the following conditions a) when the furnace door is broken or the furnace door cannot be locked; b) when not placed in the swivel and glass turntable; c) when there is no digested item in the device; d) when the digestion tank is empty; e) when the digestion tank is only filled with clean water; 4.3 .3.2 security matters a) The current carrying capacity of the device shall be not less than 10A and shall be reliably grounded; b) Do not cover the furnace body during use to keep it cool; c) no metal objects shall be placed in the furnace; d) In order to prevent damage caused by starting the device during no-load, the glass can be filled into the furnace with water, and it should be taken away when using the device; 4.3 .3.3 device-specific This device is only used in the CODcr, TP, TN test, the sample is digested, must be used strictly in accordance with the instructions of this manual, can not be used for other purposes. V. Digestion and testing methods 5. 1 Chemical Oxygen Demand (CODcr) 5. 1.1 reagent preparation a) Potassium dichromate digestion solution (1/6K2Cr2o7=0.400mol/L): Weigh the reference or superior pure potassium dichromate 19.60g dried at 120 °C for 2 hours in a 1000mL beaker and dissolve in about 500mL distilled water. Add 250 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid slowly under stirring. After cooling, transfer to a 1000 mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with distilled water, and shake well. The solution has a potassium dichromate concentration of 0.400 mol/L. It is used to measure water samples with a COD concentration of 1000-2500 mg/L (including water samples to be diluted above 2500 mg/L). Further, 9.806 g, 2.45 g of potassium dichromate (the same amount of sulfuric acid added) was weighed into 0.200 mol/L, 0.050 mol/L potassium dichromate digestion solution according to the above method. It is used to determine water samples with COD concentrations between 50 and 1000 mg/L and ≤50. b) Masking agent: Mercury sulfate (Hg2S04) crystal or powder. c) Catalyst: Weigh 10g of silver sulfate (Ag2S04) and dissolve it in 1 liter of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2S04) and shake well. d) Test the ferritic indicator: Weigh 1.485 g of phenanthroline (C12H8N2·H20) and 0.695 g of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4·7H2O) dissolved in distilled water, diluted to 100 mL, and stored in a brown bottle. e) Ammonium ferrous sulfate standard solution [(NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H20≈0.1mol/L]: Weigh 39.5g of analytically pure ammonium ferrous sulfate dissolved in distilled water, and slowly add 20mL of concentrated sulfuric acid while stirring. After cooling, transfer to a 1000 mL volumetric flask, dilute with distilled water to the mark, and shake well. Before use, calibrate with potassium dichromate standard solution. Further, 19.8 g and 3.95 g of ferrous ammonium sulfate (the same amount of sulfuric acid added) were weighed into 0.05 mol/L, 0.01 mol/L ammonium ferrous sulfate solution according to the above method. Calibration method: Accurately absorb 5.00mL, potassium dichromate standard solution in 150mL conical flask, add distilled water to dilute to about 30mL, slowly add 5mL concentrated sulfuric acid, and mix. After cooling, add 2 drops of the test ferritic indicator to titrate with ammonium ferrous sulfate solution. The color of the solution is from yellow to greenish red to brown. C[(NH4)2Fe(S04)2]=0.400x5.00V [In the formula: C-concentration of the ammonium ferrous sulfate standard solution (mol/L). V - the amount of ammonium ferrous sulfate standard titration solution (mL). 】 f) Potassium hydrogen phthalate standard solution: Weigh 0.8502g of reference potassium hydrogen phthalate in double distilled water, dissolve it and transfer it to 1000mI. Dilute the volumetric flask with double distilled water to the mark and shake well. The standard COD value is 1000 mg/L. 5. 1.2 Test steps a) Accurately absorb 5.00ml of uniform water sample (two blanks should be made for each batch of water sample at the same time of testing) in the digestion tank, add 1g masking agent (water sample without chloride ion can be added), shake well to make CI Completely complex with Hg++ (if the masking agent is completely dissolved, ie the CI content is too high, add masking agent until the masking agent is still insoluble), 5.00ml digestion solution (Note), 5.00m1 catalyst, shake uniform. b) Tighten the sealing cover and place the digestion tank evenly around the glass turntable of the furnace chamber to close the furnace door. c) Digest the sample according to the “5.2.1, 5.2.2†method. d) After the digestion is completed, open the furnace door and cool it, then remove the digestion tank from the furnace. When the liquid in the tank is cooled to room temperature (if it needs to be cooled, it can be placed vertically into the cold water basin), and measured by titration or colorimetry. The CODcr value is obtained. 5. 1.3 Titration a) Transfer the sample solution to a 150ml Erlenmeyer flask, rinse the digestion vessel and the inner wall of the lid three times with 20mL distilled water, flush the rinse into the Erlenmeyer flask, and add 2-3 drops of the ferrous sulfate indicator to the ferrous sulfate. Ammonium standard solution back drop (Note), the color of the sputum is from yellow to greenish red to brown, which is the end point. The amount of ammonium ferrous sulfate standard solution is recorded, and the CODcr value is calculated by the following formula. b) Calculation method: CODcr (mg/L) = (V0 - V1) × C × 8 × 1000 V2 [In the formula: V0 - blank consumption of ammonium ferrous sulfate standard solution (mL). V1 - water sample consumption of ammonium ferrous sulfate standard solution (mL). C - concentration of ammonium ferrous sulfate standard solution (mo1/L). 8 - oxygen (1/2 0) molar mass (g/mo1). V2 - water sample volume (mL). 】 5. 1.4 Colorimetry a)  Add 5.00 mL of distilled water to each digestion tank with a pipette, cover with a sealing cap, shake well, and cool. b) Adjust the wavelength of the preheated spectrophotometer to 600 nm, adjust “100%†and “0.0†as required, and test after meeting the requirements. c) Transfer the solution to a 30 nm cuvette (same blank), perform colorimetry, and note the absorbance. d) Calculation method: Calculate the slope based on the plotted standard curve. CODcr = A·F·K [In the formula: A - is the absorbance of the sample. F - is the dilution factor. K—— is the inverse of the slope of the curve, that is, the CODcr value when A=l. 】 e) Preparation of standard curve: 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 mL of potassium hydrogen phthalate standard solution were respectively taken. In a series of 100 mL volumetric flasks, add twice distilled water to the mark and shake well. The COD values ​​are 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, and the stock solution is 1000 mg/L standard use solution. Sampling and digesting according to the test step, colorimetric, drawing a standard curve. Find the linear regression equation. [ Note: The concentration of digestive solution (K2Cr207) and the concentration of ammonium ferrous sulfate (NH4) 2Fe(SO4)2 are determined according to the CODcr concentration (see Table 3). 】 Table 3 is as follows  5. 2 total phosphorus (TP) a) Sulfuric acid (H2SO4): l+l b) 5% (m/V) potassium persulfate: 5 g of potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) is dissolved in distilled water and diluted to 100 ml. c) 10% ascorbic acid: 10 g of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6) was dissolved in distilled water and diluted to 100 ml. Store in a brown bottle and use it for a long time if it does not change color. d) Molybdate solution: 13 g of ammonium molybdate [(NH4)6Mo7O24·4H20] is dissolved in 100 ml of distilled water, and 0.35 g of bismuth potassium tartrate [KSbC4H406·l/2 H20] is dissolved in 100 ml of distilled water with constant stirring. The ammonium molybdate solution was slowly added to 300 ml of (1+1) sulfuric acid, and a solution of bismuth potassium tartrate was added and mixed uniformly. Store in a cold place in a brown bottle and stabilize for at least two months. e) Turbidity-chroma compensation solution: Mix two volumes of (1+1) sulfuric acid and one volume of 10% (rn/V) ascorbic acid solution. This solution was formulated for use. f) Phosphorus standard solution: 1 Stock liquid: Weigh 0.2187g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2P04) dried at 110 °C for 2 hours, dissolve it in a small amount of distilled water, transfer it to a 1000ml volumetric flask, add 5ml of (1+1) sulfuric acid, dilute to the standard with distilled water. line. 1.00ml This standard solution contains 50.00 μg of phosphorus. 2 Use solution: Transfer 10.00ml of phosphorus standard stock solution to a 250ml volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with distilled water and mix. 1.00 ml of this standard solution contains 2.00 μg of phosphorus. 5. 2.2 Test steps a) Pipette 25ml of water sample (the same blank) in the digestion tank. (If the phosphorus concentration in the sample exceeds 0.6mg/L, take less water samples or dilute and sample again). Add 4 ml of potassium persulfate. b) Tighten the sealing cover and place the digestion tank evenly around the glass turntable of the furnace chamber to close the furnace door. c) Digest the sample according to the “5.2.1, 5.2.2†method. d) After the digestion is completed, open the furnace door and cool it, then remove the digestion tank from the furnace. When the liquid in the tank is cooled to room temperature (if it needs to be cooled, put it into the cold water basin), move the liquid to the 50ml colorimetric tube. Rinse the inner wall of the digestion tank and the lid with a small amount of distilled water 2 or 3 times. The rinse solution is incorporated into the colorimetric tube, diluted to the mark, and shaken. e) Color development: Add 1 ml of ascorbic acid to the colorimetric tube, mix well, and mix well with 30 ml of molybdate solution after 30 seconds. f) Test: After standing at room temperature for 15 minutes, remove part of the solution to a 30 mm cuvette. At the wavelength of 700 nm of the spectrophotometer, adjust the “100%†and “0.0†according to the colorimetric operation. As a reference, the absorbance was measured, the reading was recorded, and the phosphorus content was found from the working curve. g) Drawing of the working curve: Take 7 colorimetric tubes and add the standard use solution of phosphorus to 0.00, 0.50, 1.00, 3.00, 5.00, 10.0, 15.0 and add water to 15m1. Then, the test was carried out according to the test step, and after subtracting the absorbance of the blank test, the working curve was plotted against the content of the corresponding phosphorus. h) Calculation method : The total phosphorus content is expressed in C (mg/L) and is calculated by the following formula. C = M/V [In the formula: M - the measured phosphorus content, μg. V——Measure the volume of water sample, ml. Note: 1. If the sample has turbidity or chromaticity, prepare a blank sample (diluted with water to 50mi after digestion) and then add 3 ml turbidity-chroma compensation solution to the sample, but without adding ascorbic acid solution and molybdate solution. . The absorbance of the blank sample was then subtracted from the absorbance of the sample. 2. If the room temperature is lower than 13 ° C when color development, it can be developed in a water bath of 20 to 30 ° C for 15 min. 】 5. 3 total chlorine (TN) a)  Ammonia-free water: 0.1 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid was added per liter of distilled water, and it was redistilled in a full glass distiller, and the distillate was collected in a glass vessel. b) Alkaline potassium persulfate: Weigh 40g potassium persulfate (K2S2O8), 15g sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and let it be in ammonia-free water and dilute to 1000ml. The solution is stored in a polyethylene bottle and can be stored for one week. c) 10% hydrochloric acid (HCI) d) Potassium nitrate standard solution: 1 Stock liquid: Weigh 0.722g of potassium nitrate (KN03) dried at 105-110 °C for 3h, dissolve it in non-ammonia water, transfer it to a 1000 ml volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark. 1.00 ml of this standard solution contains 100 μg of nitrate nitrogen. If 2ml of chloroform is added as a protective agent, it can be stable for at least 6 months. 2 Use liquid: The stock solution was diluted 10 times with ammonia-free water, and 1.00 ml standard solution contained 10 μg of nitrate nitrogen. Formulated when used. 5.3.1 Test procedure a) Adjust 10ml of water sample with pH value of 5-9 (if the nitrogen content in the water sample exceeds 4mg/L, take less water sample or dilute and sample again) in the digestion tank, add 5ml alkaline potassium persulfate. Solution. b ) Tighten the sealing cover and place the digestion tank evenly around the glass turntable of the furnace chamber to close the furnace door. c) Digest the sample according to the “5.2.1, 5.2.2†method. d) After the digestion is completed, open the furnace door and cool it, then remove the digestion tank from the furnace. When the liquid in the tube is cooled to room temperature (if it needs to be cooled, it can be placed vertically into the cold water basin) plus 10% hydrochloric acid 1m1 to dissolve with ammonia-free water. Up to 25ml. e) Pipette part of the solution into a 10mm quartz cuvette, and adjust the absorbance at wavelengths of 220nm and 275nm with ammonia-free water as reference after the colorimetric operation of the spectrophotometer "100%" and "0.0" are met. Record the reading and calculate the corrected absorbance A, then check the calibration curve according to the value of A and calculate the total nitrogen (in terms of N03-N). A=A220-2A275 f) Drawing of the calibration curve (the specific operation is as follows: take 7 colorimetric tubes, add nitrate nitrate standard solution 0.00, 0.10, 0.50, 1.00, 2.50, 5.00, 10.00 ml, plus Ammonia water is diluted to 10.00ml. According to the above steps, the absorbance is measured, and the corrected absorbance As and the zero-concentration corrected absorbance Ab of the other calibration series except the zero concentration are determined by the following formula and the difference is Ar As= As220 One 2As275 Ab= Ab220-2Ab275 Ar=As-Ab [In the formula: As220 - the absorbance of the standard solution at a wavelength of 22 nm. As275 - the absorbance of the standard solution at a wavelength of 275 nm. Ab220 - Absorbance of the zero concentration (blank) standard solution at a wavelength of 220 nm. Ab275 - Absorbance of a zero concentration (blank) standard solution at a wavelength of 275 nm. A calibration curve was drawn by the Ar value and the corresponding N03-N content (μg). 】 )  g) Calculation method j The total nitrogen content is expressed in C (mg/L) and is calculated by the following formula. C = M/V [In the formula: M - the measured phosphorus content, μg. V——Measure the volume of water sample, ml. 】 Sixth, failure analysis and elimination Simple Failure Analysis and Troubleshooting (see Table 4 under).      Seven, maintenance and maintenance  7.1 power outage maintenance When cleaning, maintaining, or maintaining the unit, unplug the power cord from the outlet to avoid electric shock. 7.2 furnace chamber cleaning Always keep the oven cavity clean to achieve the best sample digestion, such as spills in the cavity, dry with a soft cloth; if it is too dirty, wipe it with a soft detergent. 7.3 Maintenance door It is normal to condense water droplets around the door. Use a soft cloth to clean it. Keep the door seal clean and check the door locks regularly. 7.4 furnace surface cleaned Wash with a soft detergent and warm water, then wipe with a soft cloth. Do not allow water droplets to penetrate into the furnace joint or ventilate the air passage. The control surface wrench can only be cleaned with a soft cloth. It should not be cleaned with an aqueous solution such as detergent. Eight, acceptance and storage  8 .1 acceptance a)  After unpacking, you should take out the instruction manual and check whether all the accessories are complete and the specifications are consistent according to the “list of accessoriesâ€; b) Carry out the acceptance operation according to the instruction manual (put a 250ml of water in the furnace to see if it is warming up). 8 .2 storage When the device is not used before or after unpacking, it should be stored under the following conditions: a)  Ambient temperature: 0~40; b) Relative humidity: ≤ 80% RH; c) Atmospheric pressure range: 86 kPa to 106 kPa  . Short range distance sensors from JRT combine highly precise measurement results with quick and reliable response. Short distance sensor module use single-transmit and single-receive measurement technology and can be used to measure a distance or monitor the slow moving objects. For the laser pointer distance measure, also called optical range sensor, can measure legth, width, depth. Laser rangefinder transducer with rxtx has been widely used to industries. Laser Distance Sensor Short Range,Short Range Sensors,Oem Laser Distance Sensor,Distance Sensor Laser Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jrt-measure.com
![]()
![]()

![]()