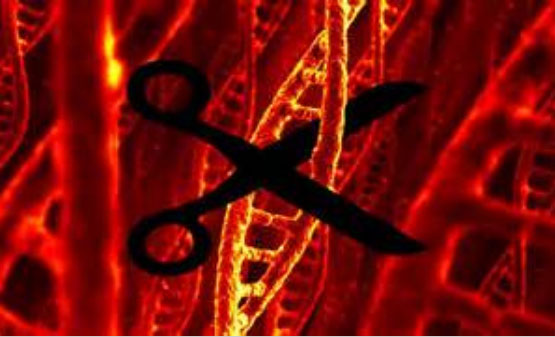
IBS scientists have discovered the smallest member of the CRISPR-Cas9 family to date, and studies have shown that it can edit mutant blinding genes through adeno-associated viruses. Researchers at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and Seoul National University in Korea have designed the smallest CRISPR-Cas9 and delivered it to muscle cells and mice via adeno-associated virus (AAV). In the eyes, to edit the genes that cause blindness. The findings, published in Nature Communications, from the C. jejuni (CjCas9) system, may become a new tool for the treatment of general diseases and "incurable" diseases in the future. CRISPR-Cas9 is red-purple, and as a "genetic scissors" protein, Cas9 needs to be cleaved at the precise target gene position under the guidance of a targeting RNA. The CRISPR-Cas9 complex needs to be delivered by plasmid or virus in order to reach the target DNA. KIM Jin Soo, director of the IBS Genomics Engineering Center, explained: "AAV is an effective and safe vector for the expression of target genes in vivo and has been widely used in gene therapy." In its natural state, Cas9 is an immune weapon for bacteria that cuts viral DNA that can damage bacteria. The most common CRISPR-Cas9 technique uses Cas9 derived from S. pyogenes. However, this protein consists of 1,368 amino acids and is too bulky to be packaged and delivered via AAV. Even if scientists divide it into two parts, each wrapped in a different virus, there will be other problems, such as requiring twice the amount of virus, the activity is smaller than the complete Cas9. Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 can also be used for gene editing and is slightly smaller (1,053 amino acids), so it can be transmitted by AAV, but this Cas9 does not have enough space to load other proteins. In this latest study, the researchers found that CjCas9 is the right size and efficient. This protein has 984 amino acids and can be packaged into AAV along with multiple targeting RNAs and fluorescent reporter genes. Tissue Underpads are disposable absorbent pads that are placed under a
patient to protect bedding, furniture, or other surfaces from bodily
fluids, such as urine or blood. They are made of a soft, non-woven
material that is gentle on the skin and have a waterproof backing to
prevent leaks. Tissue underpads come in a variety of sizes and
absorbency levels to meet the needs of different patients and
situations. They are commonly used in hospitals, nursing homes, and home
care settings. Tissue Underpads,Underpads For Incontinence,Medical Waterproof Incontinence Underpads,Incontinence Bed Pads With Breathable Film Honghu Danielle Sanitary Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.daniellecn.com