ICAM-1 and IL-8 are up-regulated in HL-MVEC (Fig. 2) Identification of anti-inflammatory compounds based on endothelial cell screening Cyanobacteria are blue-green algae that have a very diverse metabolite. Some of these metabolites have good therapeutic potential and are currently being studied for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. 1,2,3 We screened compounds with anti-inflammatory properties from cyanobacteria using the methods described above. HL-MVEC was previously treated with different components extracted from Nostoc cyanobacteria and then stimulated with 0.4 ng of human TNF-alpha protein. After 18 hours, ICAM-1 was up-regulated using the AlphaLISA technique on the SpectraMax Paradigm platform, and the cell culture supernatant was further analyzed for IL-8 levels. We found that the cyanobacteria 8721, component 6 (Figure 3) significantly reduced the production of ICAM-1 and showed anti-inflammatory activity. This component also significantly reduced the expression and secretion of IL-8 (data not shown). The cytotoxicity test of the components was also performed before the AlphaLISA test, indicating that the cytotoxicity was small and negligible. Screening of anti-inflammatory active ingredients in cyanobacteria (Figure 3) to sum up Vitamins are a kind of trace organic substances that humans and animals must obtain from food in order to maintain normal physiological functions. They play an important role in the growth, metabolism, and development of the human body. In the body, this kind of substance can neither be a raw material for body tissue nor a source of energy, but a kind of regulating substance, which plays an important role in material metabolism. Vitamin C,vitamin b3,vitamin raw material Xi'an Natural Field Bio-Technique Co., Ltd. , https://www.naturalfty.com
Molecular Devices' SpectraMax® Paradigm® Multi-Function Detection Platform is the only user-upgradeable microplate inspection platform on the market that allows users to configure real-time functions in less than two minutes. If you need to use Alpha technology, users can upgrade themselves at any time. The SpectraMax Paradigm platform enables rapid quantification of TNF-alpha factors and enables highly sensitive screening of anti-inflammatory metabolites by quantifying cytokines in TNF-alpha-stimulated human endothelial cells.
AlphaLISA® is a microbead-based homogeneous detection technique for studying the interactions between molecules in microplates. It can be used for quantification of cytokines as well as screening for compounds having anti-inflammatory activity. Compared to traditional ELISA methods, ELISA requires multiple washing steps, and washing operations can destroy adherent cells. AlphaLISA does not require washing, reducing cell loss, making the experimental results smaller in SD and more accurate.
TNF-alpha purification and quantification
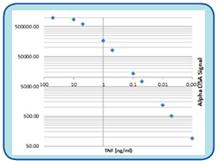
First, it is necessary to obtain purified TNF-alpha protein for stimulating endothelial cells to produce an inflammatory response. For this purpose, human TNF-alpha factor is expressed in Pichia pastoris yeast. The advantage of using yeast is that it can express both large amounts of recombinant protein without endotoxin that interfere with cell level experiments. We can purify 10-20 mg of biologically active protein from each liter of yeast culture. The SpectraMax Paradigm platform uses the AlphaLISA method to quantify proteins down to the pmol level (Figure 1). The 384-well plate can be tested in 2 minutes using the software's built-in optimized test program.

We then developed an AlphaLISA assay to measure the levels of pro-inflammatory factors produced by endothelial cells after TNF-alpha stimulation. Treatment of human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVEC) with human purified TNF-alpha protein purified above induced intercellular adhesion factor 1 (ICAM-1) expression. ICAM-1 was up-regulated after 18 hours of incubation. The expression level of ICAM-1 was quantified using AlphaLISA (Fig. 2A).
Endothelial cells express IL-8 secretion after stimulation with TNF-alpha or LPS. IL-8 is a chemotactic protein of neutrophils, and neutrophils can infiltrate inflamed tissues in the body. Therefore, quantification of IL-8 secreted by endothelial cells can provide valuable information on the proinflammatory status of vascular endothelial cells in vitro. To assess the level of secreted IL-8, we analyzed the processed HL-MVEC cell culture supernatant samples using AlphaLISA (Fig. 2B).
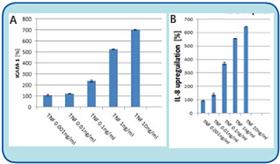
After 18 hours of TNF-alpha treatment, the up-regulation levels of ICAM-1 (A) and IL-8 (B) in HL-MVEC cells were detected using the AlphaLISA method of the SpectraMax Paradigm platform.
AlphaLISA was used to analyze the upregulation effect of ICAM-1 in each component of cyanobacteria. Components 8721, 6 significantly reduced expression of ICAM-1.
The SpectraMax Paradigm platform in conjunction with AlphaLISA provides a powerful tool for screening novel therapeutics using endothelial-based, pathologically relevant models. High sensitivity, high speed, up to 1536-well board compatibility, and built-in pre-optimized inspection programs make user operations simpler and faster. SpectraMax Paradigm is the best choice for screening drugs with Alpha technology.
Acknowledgement
Finally, we would like to thank Maren Plüger Anita Eigner, Maria Hirschler, Linda Kotnik, Katrin Fuchslueger, Julia Schweiger, Christoph Wiesner, Andreas Eger, Wolfgang Schütt, Harald Hundsberger of IMC University, and Jiri Kopecky of the Czech Academy for their generous data.
Reference material
1. Rasool, M.; Sabina, EP; Lavanya, B. Biol Pharm Bull 2006, 29(12), 2483
2. Romay, C.; Armesto, J.; Remirez, D.; Gonzalez, R.; Ledon, N.; Garcia, I. Inflamm Res 1998, 47(1), 36.[31]
3. Prinsep, MR; Thomson, RA; West, ML; Wylie, BL J Nat Prod 1996, 59(8),
From the point of view of chemical structure, various vitamins are very different or even unrelated. Therefore, vitamins are usually classified according to their physical properties. They can be divided into fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamin A, D, E, K, etc.) and water-soluble vitamins ( Such as vitamin C, vitamin B1, B2, B6, B12, pantothenic acid, PP, biotin, folic acid, choline, etc.). Water-soluble vitamins are easily soluble in water but not soluble in organic solvents. They are stored in the body after absorption. Excessive amounts are mostly eliminated in the urine; fat-soluble vitamins are easily soluble in organic solvents but not in water. They can be absorbed by the body with fat and stored in the body, and the excretion rate is not high.
From the perspective of obtaining methods, vitamins can be divided into natural products and chemical synthetic products. Because natural vitamins are limited by raw materials and extraction technology, their yields are low, and their prices are high. Therefore, chemical synthesis takes the lead, accounting for about 80% of the total vitamin output. Among the various segments of the vitamin industry, vitamin B, vitamin E, vitamin C and vitamin A have the largest market shares, 33%, 30%, 21% and 13% respectively. Other vitamins have a smaller market share, accounting for only 3%.
Application of AlphaLISA Screening Technology on SpectraMax Paradigm Multi-Function Detection Platform
AlphaLISA screening technology
Application on SpectraMax Paradigm Multi-Function Detection Platform
Inflammation: The body's response to infection, irritation, or other injury. It is usually accompanied by an increase in endothelial chemokines and expression of adhesion molecules. This can lead to extensive neutrophil infiltration. The study of novel Anti-Inflammatory compounds can down-regulate the expression of these factors and reduce tissue damage, which has broad therapeutic prospects. However, we need a fast and highly sensitive platform to screen these therapeutic anti-inflammatory compounds to quantify the factors that cause inflammation.
TNF standard curve (Figure 1)
The SpectraMax Paradigm platform can quantify TNF-alpha as low as pmol and can be detected in four orders of magnitude.
Proinflammatory cytokine test