When we are in a different place, it is inevitable to learn a few dialects or foreign languages ​​to communicate with local people. Fortunately, when the language is not available, we can express the meaning by gestures or pictures. However, if we enter the brain, how can we communicate with the owner, the neuron ? This group of elves may be smarter than aliens, and certainly more secretive than aliens. Although they are located in the brains of each of us, they seem to come from a distant world; we never know each other. So, can we understand the signals from the neurons, how can we communicate with this group of "exotic creatures" from the body? This seems to be a problem. Scientists often call themselves explorers; they are always exploring the unknowns of the world. They are also challengers and always want to solve problems that seem impossible to solve. With these identities, they entered the mysterious land of the brain, trying to solve the problem of how to talk to neurons. This time they acted as translators, translating signals from neurons into languages ​​we can understand. Humans communicate by sound, and neurons communicate through an electrical signal called the action potential . Each neuron roots will extend many long protrusion (comprising: axons (Axon) and the dendrites (Dendrite) and surrounding nerves to establish contact element hand in hand they form a complex network to transmit electrical signals. It is transmitted in the 'cable' between these neurons. Figure 2 A neuron in the retina, the action potential is transmitted between axons and dendrites We can use an ammeter to test the current in the circuit, so we also want to use it to read the electrical signal in the neuron. This technique of studying biological functions by recording biological electrical signals is called electrophysiology . However, the neurons are too small, and the sound of his screaming is too weak. We can't hear them with ordinary galvanometers. Perhaps, when the neurons come to a chorus, we can hear their melody. Scientists of course also thought of this, so they made the right electrodes to record the response of the neuron population. Electroencephalogram ( EEG ) is the installation of a number of metal electrodes on the scalp of the brain. These electrodes can combine the electrical signals of multiple neurons in the brain and present them to humans. Through EEG, we can roughly know the voices of neurons in the brain. In turn, it provides a basis for us to diagnose brain diseases and determine the activity state of the brain.    However, this is not enough for us to communicate more deeply with neurons; because, we only hear the chorus of neurons, we still can't know what each neuron is saying. In order to hand the microphone to the hands of each neuron, the scientists conducted countless experiments. In the end, they listened to a small group of neurons by inserting a slender metal electrode into the animal's brain. The extracellular recording (extracelluar recording) is a recording method for recording groups of neurons extracellularly. In this way, the action potentials emitted by each neuron can be recorded by this sensitive electrode. Just as everyone has their own tone, each neuron has its own unique action potential. By analyzing the different shapes of the action potentials, we can distinguish the different sounds emitted by different neurons. Some neurons are ignorant wise men who only make their own decisive opinions at critical moments. And there are some neurons, like the endless singers, who are always giving action potentials and contributing their strength to the atmosphere.      Now, scientists can not only know what each neuron is saying, they can even analyze words and phrases in neuron language. Why do we have to study the language of neurons so carefully? Because only knowing the basic composition of a language, we can imitate them to speak more deeply to understand their meaning. Neuronal action potential is made more ion channel currents (ion channel current) thereof. Ion channels are components of neuronal cell membranes. Thousands of ion channels are open and closed, creating innumerable tiny channel currents that converge at a certain point in time to form an action potential. Of course, to hear the sound of each voice, we must be very close to the neurons and cannot be affected by the speech of other neurons. The patch clamp technique is an electrophysiological technique that records the current of a single neuron ion channel. This time the scientists invented a glass microelectrode that can hold the neurons tightly . When the glass microelectrode is close to the neuron, we gently breathe a breath in the glass electrode and the neurons are tightly attracted by the tip of the glass electrode. In this way, we can not only record the sound of this neuron through the electrodes, but also control the tone of the neurons by changing the voltage, and then let the neurons speak a certain phrase. This way we record the current of a certain ion channel. After hundreds of years of unremitting efforts by scientists, we have been able to get a glimpse of the basic ways of communication between neurons; but when faced with the strange sounds of hundreds of millions of neurons in our brains, we are still looking at it. . Every neuron in the brain is a small elf who plays a different role in the neuron society. We tried to figure out the function of each neuron by listening to their conversations, but their language seemed too esoteric, and the way we talked to them was too shallow. So far, we have not been able to talk fluently with neurons and ask him about the mysteries of the brain. It seems that scientists must not only become a translator, but also become a special agent to crack passwords. How to read the information contained in the action potential generated by neurons, how to link this information with the function of neurons has become a difficult problem for scientists. We believe that in the near future, as technology advances, we will be able to engage in more face-to-face conversations with neurons.  references: 1. Stephen J Smith. Circuit Reconstruction Tools Today. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 October ; 17(5): 601–608. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2007.11.004 2. http://newton.umsl.edu/tsytsarev_files/Lecture02.htm 3. http:// 4. Alix Tiran-Cappello. The role of retinal direction-selective ganglion cells for the transmission of visual signals. BioSciences Master Reviews. 2012. 5. Steven D. Buckingham. Successful Patching. Bench philosophy: Patch clamping guidelines.2009. 6. Sakmann, Bert & Neher, Erwin.Single-Channel Recording.1995. Source: The Voice of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Wang Fei Introduction:
3.Color:Pure white/Normal white
4.Nutrition Organic White Garlic,Silver White Garlic,Organic White Garlic Seed,Organic White Garlic Powder shandong changrong international trade co.,ltd. , https://www.changronggarliccn.com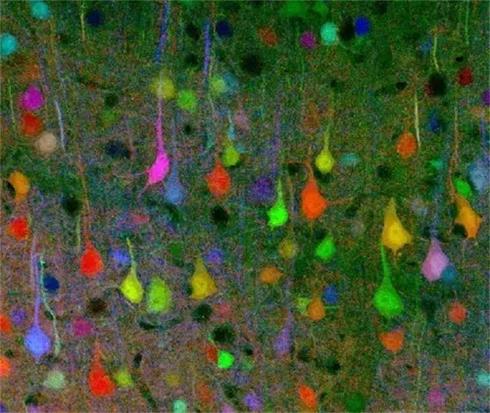
Figure 1 Neurons in the brain, different colors labeled different types of neurons 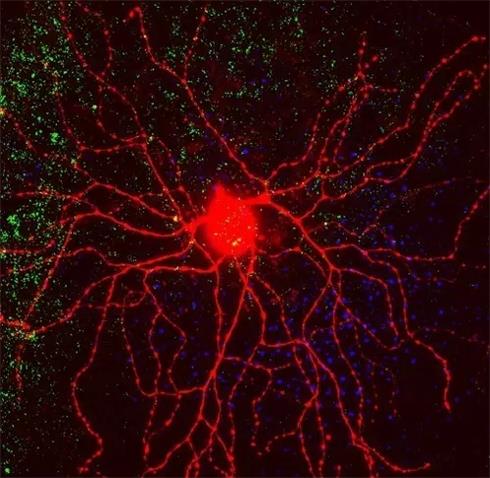

Figure 3 EEG device and recorded brain waves 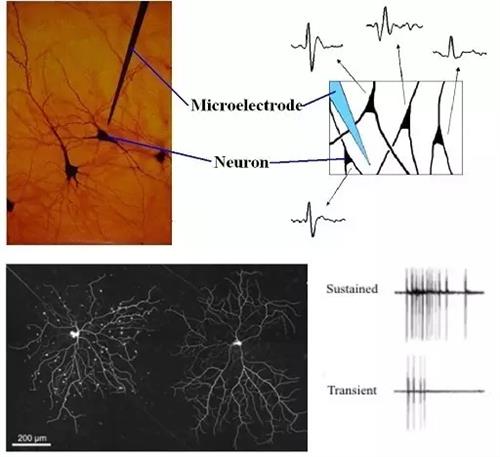
Figure 4 The extracellular metal electrode records the action potential emitted by the neuron, and the different neurons are issued in different modes. 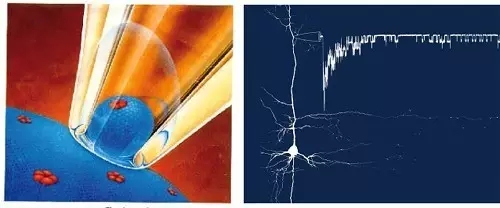
Figure 5 Patch clamp working diagram and recorded single ion channel current
Our farmland has fertile soil,sufficient sun-light,ample rainfall,and far away from urban pollution,traditional planting methods,artificial weeding,standardized pesticide residues.
Our pure White Garlic,keep freshness and nutrition to the greatest extent
With the advantages of good condition,pure flavor,strong aroma,high allicin etc.
More knowledge:
The bulb of garlic,an allium plant in the lily family.with the pungent flavor and spicy taste.spherical shape with a diameter of 3-6.5cm. The surface is covered with white and papery-skin.
The top is slightly pointed, with residual scape in the middle,many fibrous root marks at the base. The bulbous valve is slightly ovoid, with a membranous outer skin, slightly pointed at the apex, and an arcuate bulge on one side.
Specification:
1.Brand:Changrong
2.Variety:Liliaceous Vegetables
Manganese: 2% of the Daily Value
Vitamin C: 1% of the Daily Value
Selenium: 1% of the Daily Value
Fiber: 0.06 grams
Decent amounts of calcium, copper, potassium, phosphorus, iron and vitamin B1