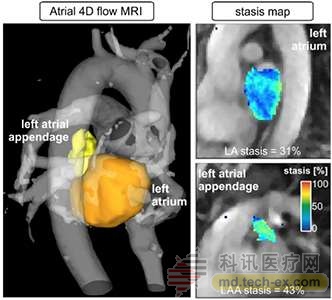
Release date: 2016-10-11 Four-dimensional flow CMR can perform three-dimensional dynamic measurement of heart and atrial blood flow. The image of stagnant blood flow derived from the left atrium and left atrial appendage is a new concept of visualization and low-flow quantification. Atrial fibrillation is the direct cause of stroke There are approximately 3.35 million atrial fibrillation patients worldwide, which is also the most common form of arrhythmia. The presence of an irregular heart does not seem to pose much of a problem, but patients with atrial fibrillation are more likely to have a stroke. Michael Markl, Lester B. and Frances T. Knight, professors of cardiac imaging at Northwestern University, said: "Atrial fibrillation is thought to be the direct cause of stroke in 20% to 30% of Americans. Although atrial fibrillation is easy to detect and diagnose, The resulting stroke cannot be easily predicted." Atrial four-dimensional CMR technique for detecting blood flow Markl is a biomedical engineer at McCormick School of Northwestern University and a professor of radiology at Feinberg School of Medicine. He developed a new imaging technology that can help predict the population at greatest risk of stroke. This breakthrough technology may lead to better treatment and prognosis for patients with atrial fibrillation. The study was supported and sponsored by the American Heart Association and the National Institutes of Health, and the results were published this month in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging. Atrial fibrillation causes a stroke because it reduces blood flow to the patient. Slow, stagnant blood flow will produce blood clots, which will follow the blood circulation into the brain and cause strokes in the patient. Markl's Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) imaging test measures the flow of blood in the heart and body. The so-called "atrial four-dimensional CMR" technology is a non-invasive technique that does not require contrast agents. The visualization process will display dynamic images of blood flow in three spatial dimensions in the form of software, which can also be integrated into current MRI equipment without the need to purchase special hardware, scanners, or existing The device is upgraded. Markl said, "We only program the scanner to get different information than what other devices can't currently produce." The device will allow you to measure blood flow, molecular diffusion, and tissue elasticity. With it, you can perform a more detailed inspection of the human body. Atrial four-dimensional CMR technology provides a more accurate risk assessment for patients In past clinical experience, doctors have used a risk scoring system to assess a patient's risk of stroke, which will take into account risk factors such as age, general health and gender. Patients who receive a high-risk assessment will be given medication to prevent blood clot formation and prevent stroke. Markl said, “Accepting these treatments can significantly reduce the risk of stroke. But it also increases the risk of blood. This is a difficult problem that doctors can't avoid. They want to reduce the risk of stroke without introducing another risk. This is especially difficult for young patients who take long-term medications. Maybe the initial risk of concomitantness is really small, but after 20 or 30 years of taking the drug, they will become more and more likely to have complications." Markl's 4D blood flow imaging technology provides a more accurate risk assessment for patients who need medication, preventing over-treatment. In a preliminary study of 60 patients and controls, Markl found that traditional scoring systems suggest that patients with high-risk atrial fibrillation may actually have normal blood flow, while patients at low risk sometimes have slow blood flow. There is a possibility of a thrombus. "About 50% or 60% of patients who are misdiagnosed as high-risk patients actually have normal blood flow," Markl said. "You can speculate that these 50% don't really require prophylactic treatment." Markl plans to follow up with AF patients to complete a long-term study to better understand the predictive power of new imaging techniques and their diagnostic value. His team is still developing algorithms and tools to help analyze visualization data more easily. Markl believes that "our current challenge lies in the complexity of the technology, and we hope to be able to integrate the tools so that we can get the test results in just a few minutes." Arrhythmia has been linked to more serious illnesses In early September, a large study by BMJ showed that irregular heartbeats (atrial fibrillation) were associated with a large number of serious illnesses, including heart attacks, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and sudden cardiac death. The findings suggest that arrhythmia is at greater risk than stroke (a known risk of atrial fibrillation), prompting researchers to call for early intervention to reduce the risk of non-stroke outcomes in such adults. We already know that atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of stroke and death, which will also consume higher medical costs and lower patient quality of life. But the link between atrial fibrillation and cardiovascular events (rather than stroke) is unclear. Therefore, the research team at the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom and the researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the United States began to quantify the association between atrial fibrillation and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, kidney (kidney) disease and death. They analyzed 104 studies involving more than nine million participants (587867 atrial fibrillation). Differences in study design and quality have been taken into account to reduce trial bias. Atrial fibrillation is associated with a large number of different disease outcomes, including all-cause mortality, ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, and increased risk of sudden cardiac death. According to the US population, the absolute risk increases include all-cause mortality for 3.8 events per 1000 participants, ischemic heart disease for 1.4 events per 1000 participants, and chronic kidney disease for 6.6 events per 1000 participants. The absolute risk of heart failure (11 events per 1000 participants) is the highest of all outcomes. Atrial fibrillation also increases cardiovascular mortality by a factor of 2, 2.3 times the risk of stroke, and 5 times the risk of congestive heart failure. Further analysis tested the degree of association between atrial fibrillation and the outcome of these diseases, which indicates the reliability of the test results. The researchers point out that many of these events will pose a greater risk than stroke, and they believe that the research they conducted further confirms that "the association between AF and cardiovascular disease outcomes is greater than stroke." Although the results of the study do not indicate There is a causal link to a non-stroke outcome, but they write, “In particular, considering the relative and absolute risk assessment, it is necessary to develop clinical risk prediction model outcomes (such as the advantages of congestive heart failure).†The researchers believe that The study may ultimately have an impact on the priorities of public health resources and the new adult atrial fibrillation interventions." Original search "Imaging stroke risk in 4-D: New MRI technique detects blood flow velocity to identify who is most at risk for stroke" Source: Sina Pharmaceutical News Portable Cable Reel,Garden Water Hose Reel,Retractable Garden Hose Reel,Wall Mounted Garden Hose Reel NINGBO QIKAI ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.hosereelqikai.com