Spinal fixation system consists of posterior spinal fixation system,minimally invasive spinal system,posterior cervical fixation system,anterior cervical plate system,laminar shapping plate system and interbody fusion cage system.
Cervical and lumbar segmental implants are the most common types of spinal internal fixation, which can be roughly divided into anterior and posterior internal fixation according to their fixed positions and surgical approaches.
The anterior cervical vertebra is mostly fixed with locking plates and fixed screws,what are mostly made of titanium alloy materials; The posterior approach was fixed using the pedicle screw and rod system.
In some cases of spinal vertebrae bone defect, it is also necessary to implant titanium cage or PEEK cages to promote bone fusion of adjacent vertebrae. The titanium mesh cage refers to a cage shaped container made of titanium alloy material, which is loaded with autologous or allogeneic bone and placed in the spinal vertebrae bone defect, which not only serves as a strength support but also plays a role in bone fusion.
spinal fracture,Pedicle Screws,Spinal Implant,Spine Implants Jiangsu Aomed Ortho Medical Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.medthofixation.com
Mammalian cells undergo tissue extraction, primary culture, subculture and other processes during the cultivation process. Subculture will be divided into cell strain culture and cell line culture according to the specific conditions. The process is briefly described as follows:
Primary culture: After excising the tissue from the animal body, it is chopped, processed by various enzymes (common trypsin), chelating agent (usually EDTA) combined with mechanical methods (pipette repeated suction), dispersed into single cells, placed in suitable The medium is cultured to allow the cells to survive, grow and reproduce. Generally, cell culture from cells taken from animal organisms and cultured within ten generations is called primary cell culture. 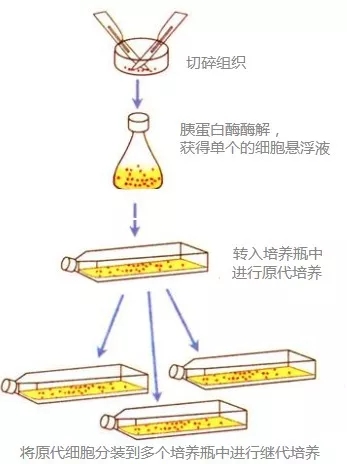
Transmitting (subsequent) culture: The primary cells are taken out from the culture flask, formulated into a cell suspension, and distributed into two or more culture flasks to continue the culture, which is called subculture.
Cell line: The cell after the first subculture is started in the primary culture, which is called the cell line. If the cell line has a limited lifetime, it is called a finite cell line. A cell line that has acquired unlimited reproduction capacity and can survive is called a continuous cell line or an infinite cell line.
Cell line: A cell population formed by single cell proliferation, isolated from a biologically identified cell line, isolated or cultured by screening, or by screening. Further, the original cell strain further separates and cultures a cell population different from the original bead shape to become a sub-plant.
Mammalian cell culture conditions
The cultivation of different mammalian cells at various stages requires basic culture conditions, which are summarized as follows:
1. Sterile and non-toxic environment : Aseptic treatment of the culture solution and all culture tools; adding antibiotics to the culture solution to prevent contamination during the culture process; periodically changing the culture solution to remove metabolites and prevent damage to the cultured cells.
2, nutrition: liquid synthetic medium contains sugar, amino acids, growth factors, water, inorganic salts, trace elements, etc.; usually also need to add plasma, serum and other natural ingredients
3. Appropriate temperature and pH: The most suitable temperature for human and mammalian cells is mostly 36 ± 0.5 °C. A suitable pH is pH 7.2-7.4.
4. Gas environment: The gas environment is generally a mixture of “95% air + 5% CO2â€. Oxygen is a necessary gas for cell metabolism, and CO2 maintains the pH of the culture solution.
The German WIGGENS CO2 incubator provides the best environment for cell growth and escorts your cell culture. 
Mammalian Cell Culture Process & Culture Conditions
Mammalian cell culture process
After the primary cell culture, the cells divide and multiply, the culture gradually increases and fills the culture space, and then contacts with each other, contact inhibition occurs, and the growth rate gradually slows down or even stops. It needs to be re-inoculated into a new culture flask for transmission (subsequent) culture.